Adenoidid Explained: Causes, Symptoms, and Care
Adenoidid is a condition that often goes unnoticed until it starts affecting daily comfort and breathing. It commonly appears in children but can also impact adults in specific situations. The issue develops when the adenoids, small immune tissues behind the nose, become inflamed or infected. Understanding adenoidid early helps prevent long-term discomfort, repeated infections, and complications related to sleep and ear health.
Understanding What Adenoidid Really Is
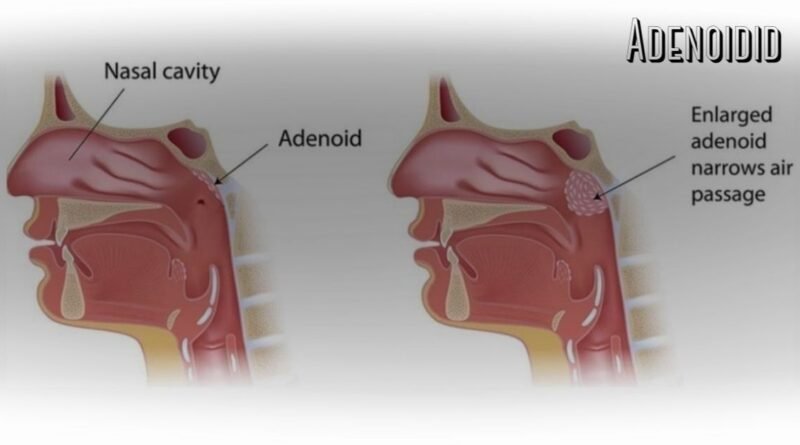
Adenoidid refers to inflammation of the adenoids, which are part of the body’s immune defense system. These tissues help trap bacteria and viruses entering through the nose. When they become overworked or infected, swelling occurs and normal airflow can be restricted.
This inflammation is usually a response to frequent infections. Instead of shrinking back after fighting germs, the tissue stays enlarged. Over time, this leads to persistent symptoms that interfere with breathing, sleeping, and overall comfort.
The condition is especially common in younger children because their immune systems are still developing. As children grow, adenoids normally shrink, which is why the problem becomes less common with age.
Will You Check This Article: Sosoactive Explained: How It Shaped Online Communities
Common Causes Behind Adenoid Inflammation
The most frequent cause of adenoidid is repeated upper respiratory infections. Colds, sinus infections, and throat infections place constant pressure on the adenoids. When exposure becomes frequent, the tissue does not fully recover between infections.
Allergies also play a role. Ongoing nasal irritation caused by dust, pollen, or environmental triggers can inflame the adenoids even without infection. This chronic irritation leads to swelling and discomfort over time.
In some cases, bacterial infections settle directly into the adenoid tissue. This makes inflammation more severe and persistent, often requiring medical treatment rather than home care alone.
Recognizing the Key Symptoms Early
One of the earliest signs of adenoidid is difficulty breathing through the nose. Mouth breathing becomes common, especially during sleep. This change may seem minor but often signals underlying obstruction.
Snoring and restless sleep are also frequent symptoms. Swollen adenoids can partially block airflow, leading to disrupted sleep patterns. Poor sleep can affect mood, focus, and energy levels, particularly in children.
Other symptoms may include frequent ear infections, nasal speech, or a constant runny nose. These signs often appear together, making it important to look at the overall pattern rather than isolated issues.
How Adenoidid Affects Daily Life
Breathing difficulties can impact daily activities more than expected. Children may struggle with concentration at school due to poor sleep quality. Adults may experience chronic fatigue or headaches linked to reduced oxygen flow.
Speech can also be affected. When nasal airflow is blocked, the voice may sound muffled or overly nasal. This can influence communication and confidence, especially in social settings.
Repeated infections associated with adenoid inflammation can lead to frequent doctor visits and missed activities. Addressing the condition early reduces these disruptions and improves overall well-being.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Diagnosis of adenoidid usually begins with a physical examination and symptom review. Doctors often look for signs such as mouth breathing, nasal congestion, and ear issues. A clear pattern of recurring symptoms helps guide diagnosis.
In some cases, imaging or a small camera may be used to assess adenoid size. This provides a clear picture of how much the tissue is blocking airflow. These methods are quick and generally well tolerated.
Accurate diagnosis matters because symptoms can overlap with sinus infections or allergies. Identifying the correct cause ensures treatment targets the real problem rather than offering temporary relief.
Treatment Options and Management Approaches
Treatment depends on severity and frequency. Mild cases often improve with medication that reduces inflammation or treats infection. Nasal sprays and antibiotics may be used when appropriate.
If allergies contribute to the problem, managing triggers becomes essential. Reducing exposure and controlling allergic responses can significantly decrease swelling and symptoms over time.
In more severe or recurring cases, surgical removal of the adenoids may be recommended. This option is usually considered when other treatments fail and symptoms interfere with daily life.
Prevention and Long-Term Care
Preventing adenoidid focuses on reducing infection frequency. Good hygiene, proper nutrition, and adequate rest support immune function. These habits help the body recover more effectively after illness.
Managing allergies early also plays a key role. Consistent care reduces chronic irritation that can inflame adenoid tissue. Environmental adjustments often make a noticeable difference.
Regular medical follow-ups ensure that symptoms are monitored. Early intervention prevents complications and supports healthy breathing patterns as children grow.
Conclusion
Adenoidid is a manageable condition when recognized early and treated appropriately. Though common in children, its effects on breathing, sleep, and overall health should not be ignored. With proper diagnosis, targeted treatment, and preventive care, most people experience significant improvement. Understanding the condition empowers families and individuals to take timely action and maintain better respiratory health.
Read More: Dollartimes.co.uk